How to Implement Automated Messaging Tools Successfully is a critical question for businesses aiming to improve communication efficiency and operational consistency. As organizations grow, manual messaging quickly becomes inefficient, error-prone, and difficult to scale. Therefore, automated messaging tools are increasingly adopted to streamline communication workflows and support long-term growth.
However, successful implementation requires more than simply activating automation features. Instead, it involves strategic planning, clear objectives, and continuous optimization. When implemented correctly, automated messaging tools transform communication into a powerful business asset.
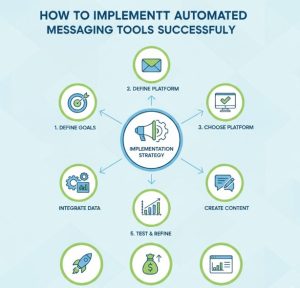
Understanding Automated Messaging Tools
Automated messaging tools are systems designed to send messages automatically based on predefined triggers, schedules, or actions. These tools reduce manual effort while ensuring messages are delivered accurately and on time.
For example, automated messaging can handle internal notifications, customer updates, reminders, and workflow alerts. Consequently, teams communicate more efficiently without constant manual input.
Why Successful Implementation Matters
While automation offers clear benefits, poor implementation can cause confusion, message overload, and reduced engagement. Therefore, understanding how to implement automated messaging tools successfully is essential for maximizing results.
Successful implementation ensures messages are relevant, timely, and aligned with business goals. As a result, communication becomes more effective rather than disruptive.
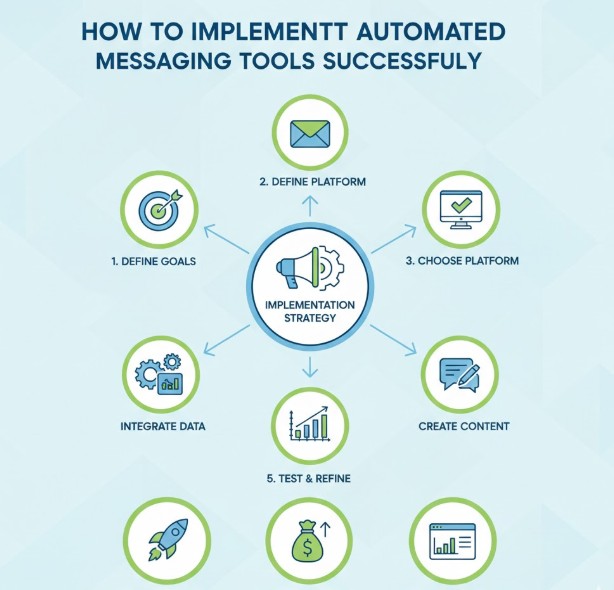
Step 1: Define Clear Communication Goals
The first step in successful implementation is defining clear objectives. Automated messaging tools should support specific communication goals rather than operate randomly.
For instance, businesses may aim to reduce response time, improve internal coordination, or increase consistency in messaging. Therefore, identifying these goals helps shape automation workflows effectively.
Step 2: Identify Key Use Cases
Not all messages should be automated. Consequently, businesses must identify high-impact use cases where automation delivers the most value.
Common use cases include task updates, deadline reminders, onboarding messages, and process notifications. By focusing on these areas, automation supports daily operations without overwhelming users.
Step 3: Map Communication Workflows
Workflow mapping is essential when learning how to implement automated messaging tools successfully. This process involves identifying when messages should be sent, who should receive them, and what information they should contain.
By mapping workflows clearly, businesses prevent redundant messaging and ensure each automated message has a clear purpose.
Step 4: Design Clear and Actionable Messages
Automated messages should be concise, clear, and action-oriented. Since recipients cannot immediately ask for clarification, clarity is essential.
For example, each message should explain what happened, why it matters, and what action is required. As a result, recipients respond quickly and confidently.
Step 5: Choose the Right Automation Triggers
Triggers determine when automated messages are sent. These triggers can include time-based schedules, user actions, or workflow changes.
Selecting the right triggers ensures messages are relevant and timely. Therefore, automation feels helpful rather than intrusive.
Step 6: Maintain Consistent Tone and Style
Consistency builds trust in automated communication. Therefore, all automated messages should follow a consistent tone, style, and formatting.
This consistency helps recipients recognize automated messages instantly and understand their purpose without confusion.
Step 7: Avoid Message Overload
One common challenge in automation is sending too many messages. While automation makes messaging easier, excessive communication reduces effectiveness.
To avoid overload, businesses should limit automation to essential messages only. Consequently, recipients remain engaged and responsive.
Step 8: Test Automation Before Full Deployment
Testing is a critical step in learning how to implement automated messaging tools successfully. Before full deployment, businesses should test workflows with small user groups.
Testing helps identify unclear messages, incorrect triggers, or timing issues. As a result, potential problems are resolved early.
Step 9: Train Teams on Automated Messaging
Even the best automation fails without proper user understanding. Therefore, teams should be trained on how automated messaging works and what to expect.
Training reduces confusion, builds trust, and encourages adoption across the organization.
Step 10: Monitor Performance and Engagement
After implementation, continuous monitoring is essential. Businesses should track message delivery, response rates, and engagement patterns.
These insights help evaluate whether automation supports communication goals effectively.
Step 11: Optimize and Refine Continuously
Automation is not a one-time setup. Instead, workflows should be reviewed and refined regularly.
As business needs evolve, automated messaging tools must adapt accordingly. Continuous optimization ensures long-term success.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Automating Without Strategy
Automation without clear goals leads to ineffective communication. Therefore, strategy must guide implementation.
Overcomplicating Workflows
Complex workflows increase the risk of errors. Instead, simplicity ensures reliability and clarity.
Ignoring User Feedback
User feedback provides valuable insights. Ignoring it limits improvement opportunities.
Benefits of Successful Implementation
When businesses understand how to implement automated messaging tools successfully, they unlock significant benefits:
-
Faster communication
-
Reduced manual workload
-
Improved consistency
-
Higher engagement
-
Scalable operations
These benefits directly support productivity and efficiency.
Automated Messaging and Business Scalability
As organizations scale, communication complexity increases. Automated messaging tools support scalability by handling growing message volumes without additional effort.
Therefore, businesses maintain communication quality even as operations expand.
Aligning Automation with Business Culture
Automation should complement company culture rather than replace human interaction. Therefore, messages should feel supportive, professional, and aligned with organizational values.
This alignment strengthens trust and acceptance among users.
Measuring Success in Automated Messaging
Success metrics may include reduced response time, fewer communication errors, and improved task completion rates.
By tracking these metrics, businesses validate automation effectiveness.
The Long-Term Value of Automation
Understanding how to implement automated messaging tools successfully delivers long-term value. Automation reduces operational friction, improves collaboration, and supports growth.
As a result, communication becomes a strategic advantage rather than a challenge.
Conclusion
How to Implement Automated Messaging Tools Successfully is not just about technology, but about strategy, clarity, and continuous improvement. When implemented thoughtfully, automated messaging tools transform communication workflows, enhance productivity, and support scalable growth.
By defining goals, mapping workflows, designing clear messages, and optimizing regularly, businesses ensure automation delivers lasting impact. Ultimately, successful implementation turns automated messaging into a powerful driver of efficiency and collaboration.