Understanding Message Delivery Failures Causes and Prevention Tech is crucial for businesses and platforms that rely on seamless communication. Message delivery failures can disrupt operations, frustrate users, and reduce trust in digital services. Whether caused by technical limitations, network issues, or system misconfigurations, preventing these failures is essential for maintaining reliable messaging experiences.
This article explores why message delivery failures occur, how they impact communication, and the technologies used to prevent them.
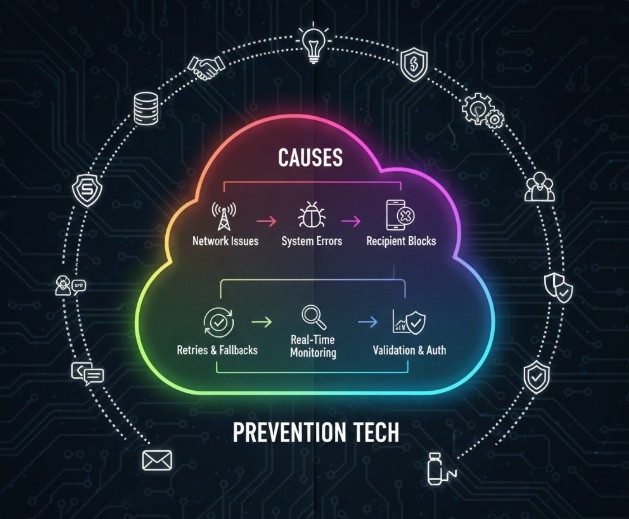
Why Message Delivery Failures Occur
Messages fail to reach their destination for many reasons, from unstable user networks to backend service problems. Internal reference: See also Common Causes of Delivery Failures.
Messaging platforms must balance speed, scalability, and reliability—any small disruption may affect delivery accuracy.
Common Causes of Delivery Failures
Message delivery failures often stem from:
1. Network Connectivity Issues
Weak cellular or Wi-Fi signals can block or delay messages.
2. Server Downtime or Overload
When backend infrastructure is under high demand, message queues may fail or slow down.
3. Device Storage or App Malfunction
Full storage, outdated apps, or corrupted files can prevent message receipt.
4. Protocol or Routing Errors
Incorrect routing rules, broken APIs, or protocol mismatches can interrupt message flow.
5. Spam or Filtering Restrictions
Platforms may block messages flagged as suspicious, even when legitimate.
Prevention Tech in Modern Messaging Systems
Modern systems use advanced prevention technologies to reduce delivery failures:
1. Automatic Retry and Queue Management
Messages are re-sent automatically when conditions improve.
2. Adaptive Routing Algorithms
Systems reroute messages through the fastest and most reliable paths.
3. End-to-End Integrity Checks
Ensures messages are not corrupted during transmission.
4. Real-Time Monitoring and Alerts
AI tools detect abnormal traffic patterns and trigger corrective actions.
5. Device-Level Optimization
Apps can compress data, adjust protocol usage, or store messages offline until the network stabilizes.
Best Practices for Ensuring Reliable Delivery
To maintain consistent delivery performance, messaging platforms apply:
-
Proactive system scaling
-
Regular device compatibility updates
-
Strong error-handling logic
-
Intelligent filtering to reduce false positives
-
Continuous testing against varied network conditions
These practices significantly reduce delivery failure rates and enhance user trust.
Conclusion
Message Delivery Failures Causes and Prevention Tech highlights the complex factors behind failed message delivery and the solutions that help prevent them. With evolving prevention technologies—such as adaptive routing, monitoring tools, and intelligent queuing—modern messaging systems continue to improve reliability and provide users with dependable communication experiences.